Tabular data
In this module you can learn:
- How to represent a table
- How to extract rows, columns and cells
- How to delete rows and columns
- How to sort columns
- How to sort
Representing a table as a list of lists:
exp gene1 gene2 gene3 gene4
1 17 19 2 10
2 2 336 3 11
3 16 21 3 12
4 17 16 1 9
table = [
['exp', 'gene1', 'gene2', 'gene3', 'gene4'], ['1', '17', '19', '2', '10'],
['2', '2', '336', '3', '11'],
['3', '16', '21', '3', '12'],
['4', '17', '16', '1', '9']
]
How would you generate this table from a text file?
We will work with the file table-1.txt available here.
T = open("table-1.txt")
table = []
for line in T:
table.append(line.split())
print table
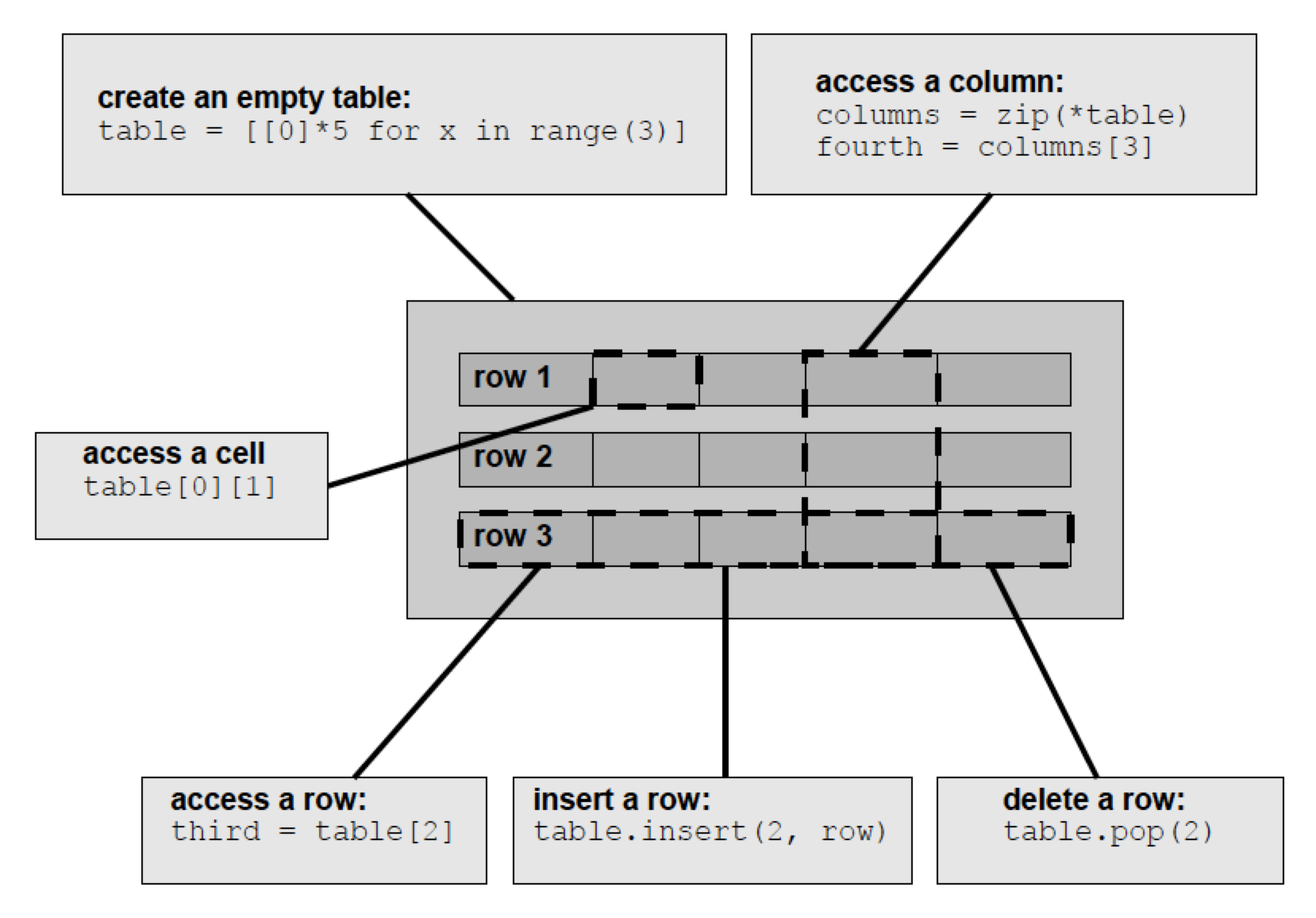
Remove a row and write the table to a tab-separated file
T = open("table-1.txt")
out_T = open("table-1.out", "w")
table = []
for line in T:
table.append(line.split())
table.pop(2)
for row in table:
out_T.write('\t'.join(row) + '\n')
out_T.close()
These command generate this table:
exp gene1 gene2 gene3 gene4
1 17 19 2 10
3 16 21 3 12
4 17 16 1 9
Insert a row and write to a tab-separated file
T= open("table-1.txt")
out_T = open("table-1.out", "w")
table = []
for line in T:
table.append(line.split())
exp5 = ['5', '17', '17', '2', '13']
table.insert(2, exp5)
for elem in table:
out_T.write('\t'.join(elem) + '\n')
out_T.close()
These command generate this table:
exp gene1 gene2 gene3 gene4
1 17 19 2 10
5 17 17 2 13
2 2 336 3 11
3 16 21 3 12
4 17 16 1 9
Transpose a table
T = open("table-1.txt")
table = []
for line in T:
table.append(line.split())
columns = zip(*table)
for elem in columns:
print '\t'.join(elem)
These command generate this table:
exp 1 2 3 4
gene1 17 2 16 17
gene2 19 336 21 16
gene3 2 3 3 1
gene4 10 11 12 9
When the argument of a function is a list or a tuple and it is preceded by *, it unpacks the list or the tuple and uses each element as an argument to the function
>>> range(*(0,10,2))
[0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
>>>
zip(*zipped) means “use each element of zipped as an argument to zip”.
>>> x = [1, 2, 3]
>>> y = [4, 5, 6]
>>> zipped = zip(x, y)
>>> zipped
[(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)]
>>> x2, y2 = zip(*zipped)
>>> x2, y2
((1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6))
>>> x == list(x2) and y == list(y2)
True
Remove a column
T = open("table-1.txt")
table = []
for line in T:
table.append(line.split())
columns = zip(*table)
columns.pop(3)
rows = zip(*columns)
for elem in rows:
print '\t'.join(elem)
This generates:
exp gene1 gene2 gene4
1 17 19 10
2 2 336 11
3 16 21 12
4 17 16 9
Remove a column (live…)
>>> T = open("table-1.txt")
>>> table = []
>>> for line in T:
... table.append(line.split())
...
>>> table
[['exp', 'gene1', 'gene2', 'gene3', 'gene4'], ['1', '17', '19', '2', '10'], ['2', '2', '336', '3',
'11'], ['3', '16', '21', '3', '12'], ['4', '17', '16', '1', '9']]
>>> columns = zip(*table)
>>> columns
[('exp', '1', '2', '3', '4'), ('gene1', '17', '2', '16', '17'), ('gene2', '19', '336', '21', '16'),
('gene3', '2', '3', '3', '1'), ('gene4', '10', '11', '12', '9')]
>>> columns.pop(3)
('gene3', '2', '3', '3', '1')
>>> rows = zip(*columns)
>>> rows
[('exp', 'gene1', 'gene2', 'gene4'), ('1', '17', '19', '10'), ('2', '2', '336', '11'), ('3', '16',
'21', '12'), ('4', '17', '16', '9')]
Replace a column
T = open("table-1.txt")
table = []
for line in T:
table.append(line.split())
columns = zip(*table)
columns.pop(3)
columns.insert(3, ['gene3', '20', '20', '20'])
rows = zip(*columns)
for elem in rows:
print '\t'.join(elem)
The resulting table:
exp gene1 gene2 gene3 gene4
1 17 19 20 10
2 2 336 20 11
3 16 21 20 12
Sorting
Python lists are good for sorting using the list’s sort() method
>>> L = [1,5,7,8,9,2,3,6,6,10]
>>> L.sort()
>>> L
[1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
Sort in reversed order
>>> L.reverse()
>>> L
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1]
Methods of lists MODIFY the lists in place
The sorted() built-in function
>>> L = [1,5,7,8,9,2,3,6,6,10]
>>> newL = sorted(L)
>>> newL
[1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
Sort in reversed order
>>> L = [1,5,7,8,9,2,3,6,6,10]
>>> sorted(L, reverse = True)
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1]
Sorting with itemgetter
>>> from operator import itemgetter
>>> L = ['ACCTGGCCA','ACTG','TACGGCAGGAGACG','TTGGATC']
>>> itemgetter(1)(L)
'ACTG'
>>> itemgetter(1,-1)(L)
('ACTG', 'TTGGATC')
Sort a table by any column
from operator import itemgetter
data = [
[5, 10, 4, 3, 2],
[6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
]
data.sort(key = itemgetter(1))
print data
6 7 8 9 10
5 10 4 3 2
Sort a table by any column
from operator import itemgetter
data = [
[5, 10, 4, 3, 2],
[6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
]
data_sorted = sorted(data, key = itemgetter(1))
print data_sorted
Challenge #1
Sort a table, convert its elements to strings and write it to a file
See the Solution to challenge #1
Sort a table by the first column, then by the second, then by the third, and so on…
from operator import itemgetter
in_file = open("random_distribution.tsv")
# read table to floats
table = []
for line in in_file:
rows = line.split()
rows = [float(x) for x in rows]
table.append(rows)
# sort the table by second, then by third column
table_sorted = sorted(table, key = itemgetter(1, 2))
# format table as strings
for row in table_sorted:
row = [str(x) for x in row]
print "\t".join(row)
Also consider that…
table = sorted(table, key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
table = sorted(table, key=itemgetter(1,3), reverse=True)
Challenge #2
Download the file
neuron_data.txtfrom here. Generate two tables, one for primary and one for secondary neuronsThis is the content of the file
neuron_data.txt:
Primary 441.462
Secondary 29.031
Secondary 46.009
Secondary 40.932
Secondary 34.952
Primary 139.907
Secondary 82.248
Secondary 39.819
Secondary 144.143
Primary 16.385
Secondary 74.495
Secondary 93.231
Primary 355.702
Primary 53.566
Secondary 202.075
Secondary 142.301
neuron_data.txt
Primary 327.777
Secondary 99.782
Secondary 104.875
Secondary 118.54
Secondary 63.477
Secondary 76.063
Secondary 253.321
Primary 405.622
Secondary 125.41
Secondary 58.876
Secondary 226.57
Secondary 362.695
Primary 256.088
Secondary 149.753
Secondary 140.738
Secondary 214.723
See the Solution to challenge #2
Challenge #3
Sort the primary neuron’s table and show the three longest neurons
See the Solution to challenge #3
Challenge #4
Turn the table and calculate the length average
See the Solution to challenge #4
Challenge #5
Create an empty table of 10 x 10 cells.
See the Solution to challenge #5
Challenge #6
Fill the table with the numbers from 1 to 100.
See the Solution to challenge #6
Challenge #7
Save the table to a tab-separated file.
See the Solution to challenge #7
Back
Back to main page.