- Introduction
- 1. Background
- 2. Retrieving sequences
- 3. Sequence alignment
- 4. Distance-based analyses
- 5. Recombination
- 6. Maximum likelihood based analyses
- 7. Visualising trees
- 8. Time-stamped phylogenies
- 9. Bayesian reconstruction of time trees
- 10. Effective population size estimation
- 11. Structured populations
- 12. References
- Published with GitBook
Effective population size
Introduction
- Given a clock-like tree, one of the quantities we can estimate is the effective population size over time assuming a coalescent model.
- This captures the rate at which the tree branches:
- Small effective population size = high branching rate and short branches
- Large effective population size = low branching rate and long branches
What is the effective population size?
- Not simply the number of infected individuals
- For simple models
= number of infected individuals = average time between infections in the population ('generation time')
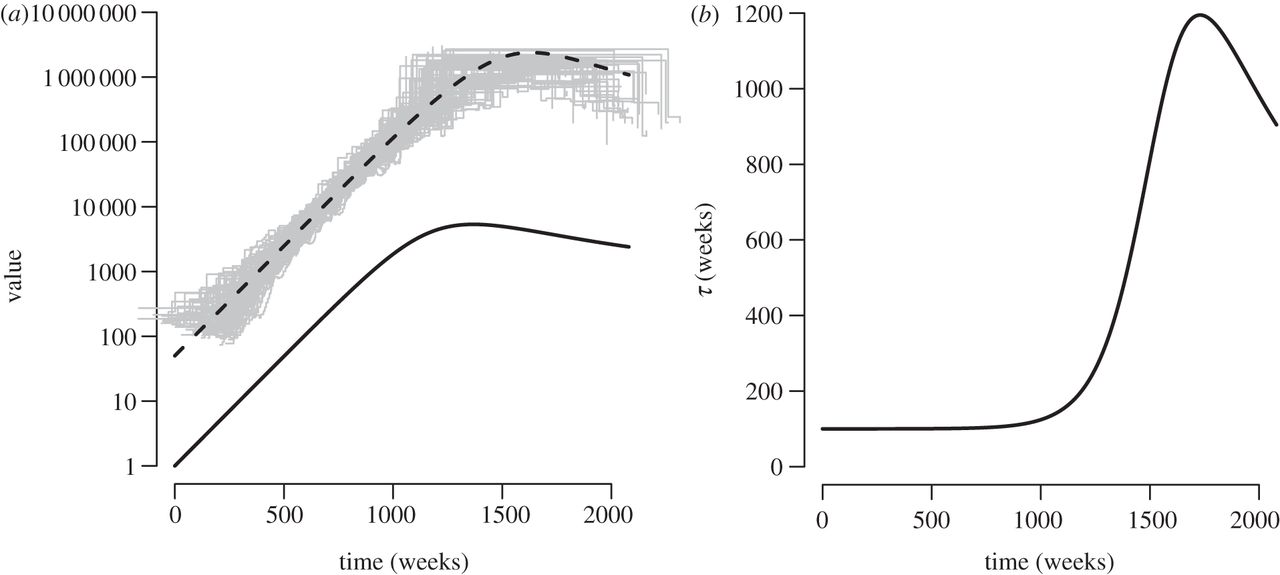
- As both change over the course of an epidemic, it is often hard to interpret effective population size epidemiologically
- However, during the epidemic growth phase, the rate of change of reflects the exponential growth rate of infected individuals
Coalescent models, birth-death-sampling models, and beyond
- Coalescent models assume the population size is changing deterministically
- R package
rcolgem
- R package
- Birth-death models allow for stochastic fluctuations in the population, but have not yet been extended to complex, nonlinear, structured populations
- R package
TreePar
- R package
- Stochastic epidemiological models are the most realistic, but have only been implemented for very simple cases
- R package
expoTree
- R package